The Danger of Misdiagnosing Silicosis
June 20, 2024
Occupational Hazard of Silicosis Among Artificial Stone Countertop Workers
June 27, 2024Blog

Why Are Artificial Stone Countertops Dangerous?
Artificial stone countertops, commonly known as quartz, engineered or synthetic stone, among other terms, have gained popularity in homes and businesses for their durability and aesthetic appeal. However, beneath their polished surface lies a health hazard that many consumers and workers in the stone fabrication industry might not be fully aware of. This blog aims to shed light on the dangers associated with artificial (or engineered) stone, particularly due to its high silica content, and why caution is necessary when dealing with this material.
Artificial stone is made by combining finely crushed stone with polymer resins, pigments, and other additives. This mixture, which can contain up to 90-95% silica, is then formed into slabs or blocks. In contrast, natural stones such as granite, slate, and porcelain contain significantly lower percentages of silica, with figures around 45%, 30%, and 15% respectively. Even marble and limestone, known for their beauty and use in construction, contain only 3% and 2% silica. The stark difference in silica content between engineered and natural stone is at the core of the health risks associated with the former.
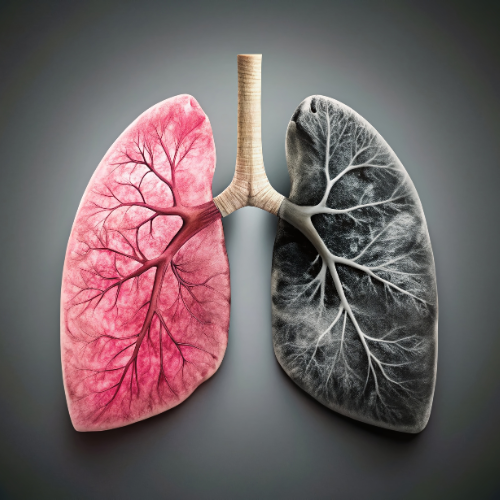
Silica, especially in its nano-sized form, poses a significant health risk when inhaled. The process of fabricating artificial stone countertops, which involves cutting, grinding, polishing, and drilling, releases hazardous levels of nano-sized silica dust into the air. This dust, often invisible to the naked eye, can lead to severe respiratory conditions, including silicosis—a lung disease that can be fatal if it progresses to the point where a lung transplant becomes necessary.
The risk is most acute for workers in the stone fabrication industry, who are exposed to large quantities of silica dust on a daily basis. Recent years have seen significant outbreaks of silicosis among these workers, highlighting the urgent need for better protective measures and awareness of the risks. However, it's not only the workers who are at risk; consumers, too, need to be vigilant. During the installation of artificial stone countertops, significant amounts of silica dust can be released, posing a health risk to anyone in the vicinity.
Furthermore, the risk doesn't end once the countertops are installed. Any future modifications or repairs that involve cutting or sanding the material can again release silica dust into the air, perpetuating the cycle of exposure.
It's crucial for consumers to be informed about the potential health hazards of artificial stone countertops. Before installation, discussions with contractors about the risks of silica dust and the precautions necessary to mitigate exposure are essential. Ensuring that workers are equipped with the appropriate protective gear and that dust control measures are in place can significantly reduce the health risks associated with artificial stone.
The allure of artificial stone countertops, with their durability and aesthetic appeal, is undeniable. However, the high silica content and the health risks it poses cannot be overlooked. Both consumers and workers need to be aware of these risks and take the necessary precautions to protect themselves and others from exposure to silica dust. By fostering a culture of safety and awareness, we can enjoy the benefits of artificial stone while minimizing its potential hazards.